5. Server requirements
This chapter describes the reference baseline configuration for the server in a Bow Pod DA system before running the Bow-2000 system software installation script. The high-level steps for configuring the server are as follows:
Select appropriate server specifications
Configure the server storage and RAID arrays
Install the server operating system and packages
Install required python packages
5.1. Server hardware and storage
5.1.1. Hardware requirements
This document describes building a system using a PowerEdge R6525 server. Contact Graphcore support for details of other supported server types or check the Approved Servers list. Other servers may have different installation requirements.
The recommended configuration of the Dell R6525 is as follows:
Dell R6525 containing dual AMD EPYC 7742 processors
16x32GB RDIMM PC4-25600 ECC registered dual-rank X4 1.2v
2x 480GB SSD-SATA 6Gbps 2.5 inch hot-swap
7x 1TB NVMe SSD PCIe 4x 3.1
Dual port Gigabit BASE-T PCIe
1x single port Mellanox ConnectX-5 EN 100Gb/s Ethernet (single Bow-2000 DA system)
2x dual port Mellanox ConnectX-5 EN 100Gb/s Ethernet (Bow Pod16 DA system)
5.1.2. Storage configuration
The recommendation is to configure two types of server storage: SSD-SATA for the operating system and NVMe SSD for data storage.
Operating system:
2x 480GB SSD-SATA drives as a RAID 1 via hardware controller
Partitioned to use ext4 file system
Data storage:
7x 1TB NVMe SSDs as a logical RAID 6 managed with MDADM
Partitioned to use xfs file system
5.1.3. Memory configuration
The DIMMs should be installed in a fully symmetric configuration, as recommended by Dell for maximum performance. The recommended configuration has 8 DIMMs per processor, as shown below.
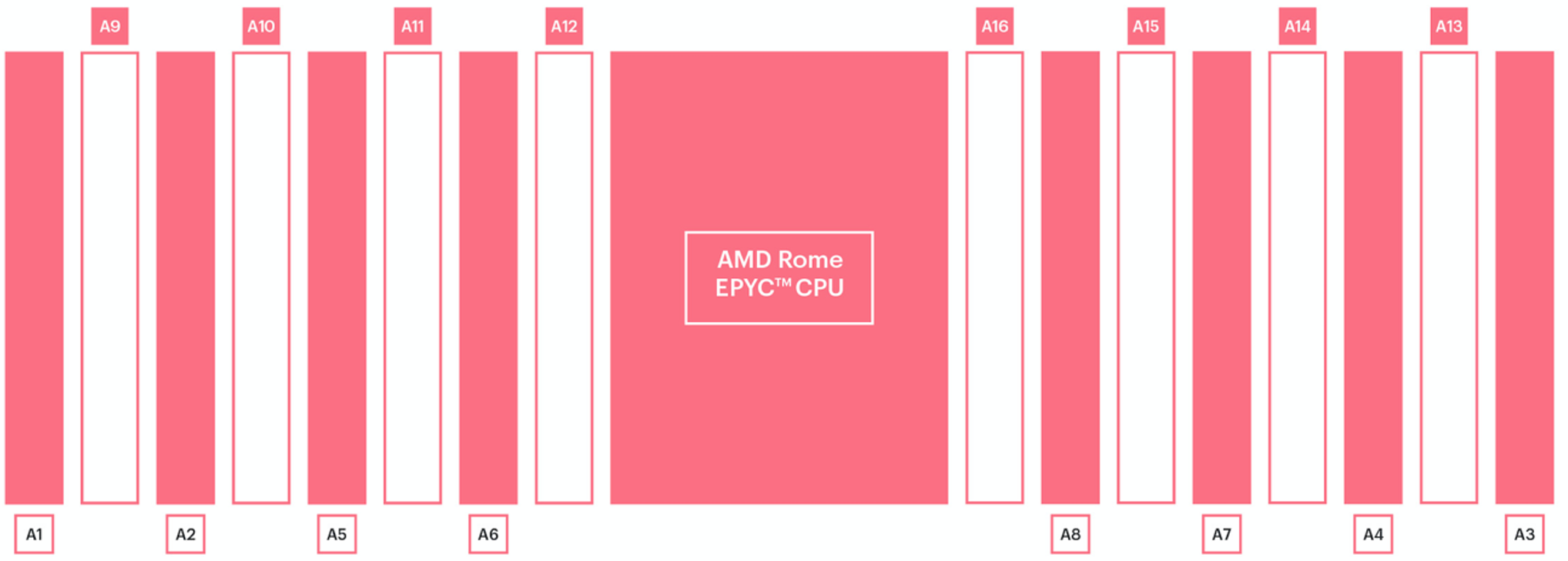
Fig. 5.1 Recommended DIMM configuration
5.1.4. BIOS configuration
Various BIOS settings can impact the performance of the system. The recommended settings are shown in the table below.
Setting |
BIOS 1.2.11 |
BIOS 1.4.8 or later |
|---|---|---|
LogicalProc |
Enabled |
Enabled |
ProcVirtualization |
Enabled |
Enabled |
IommuSupport |
Disabled |
See below |
L1StreamHwPrefetcher |
Enabled |
Enabled |
L2StreamHwPrefetcher |
Enabled |
Enabled |
MadtCoreEnumeration |
Linear |
Linear |
NumaNodesPerSocket |
4 |
4 |
CcxAsNumaDomain |
Disabled |
Disabled |
CpuMinSevAsid |
1 |
1 |
ProcCcds |
All |
All |
CcdCores |
All |
All |
EmbSata |
AhciMode |
AhciMode |
BIOS 1.4.8 or later does not configure IOMMU directly. Instead, you need to add iommu=off to the kernel boot params in /etc/default/grub and then run update-grub.
5.1.5. User application memory usage
To ensure that user application memory usage does not cause system services to be killed or otherwise affected on the host server, we strongly recommend that some form of out-of-memory protection is put in place. The purpose of this out-of-memory protection is to kill user processes before system processes (such as the V-IPU server, or DHCPD/SSHD) are affected, which will impact wider use or accessibility of the system.
Modern Linux kernels implement oom-killer, which is a line of last resort to kill processes when all memory is exhausted. However, for scientific computing/MPI workloads, they can often knock a system offline before the oom killer has an opportunity to react.
Although the mitigation will depend on the environment, some suggested options are:
Install and configure
early-oom– intended to overcome the shortcomings of the kerneloom-killer, this service monitors memory usage, and will kill processes based upon a configurable memory and swap limit.Make use of
cgroupmemory limiting – this can be used to restrict certain users/groups to a proportion of the system’s RAM. The kerneloom-killeroperates on eachcgroupindependently, meaning that theoom-killerwill react to memory pressure in a user’scgroup, while a system or defaultcgroup(containing essential system services) will be left unaffected.
5.2. Operating system and packages
This document describes the following operating systems supported by version 2.6 of the IPU-M software. Please contact your Graphcore representative or use the support portal for information about support for other operating systems or other versions of the IPU-M software.
Note
These operating systems are supported by the IPU-M software and is different to the operating systems supported by the Poplar SDK. Refer to the IPU-Machine System Software 2.6.0 Release Notes and the Poplar SDK 3.4.0 Release Notes for OS support information.
Note
If you are manually installing these packages, you can copy the list of packages into a text file, and run:
$ sudo apt update
$ xargs -a reqs.txt sudo apt-get install
where reqs.txt contains the list of packages.
5.2.1. Ubuntu 18.04 installation and packages
In order to have a stable system where IPU related software can run, the packages listed in Table 5.2 need to be installed on the system. The Bow Pod DA install script installs all of these required packages (the script checks which packages are installed and will download any that are missing). If you are running an offline install without the package repository available then you must install these packages before running the Bow Pod DA install script.
librdmacm1 |
lldpad |
mlx5_ib kernel module |
ntp (or other NTP server running on host) |
pigz |
python3-pip |
python3-venv |
rdma-core |
5.2.2. Ubuntu 20.04 installation and packages
In order to have a stable system where IPU related software can run, the packages listed in Table 5.3 need to be installed on the system. The Bow Pod DA install script installs all of these required packages (the script checks which packages are installed and will download any that are missing). If you are running an offline install without the package repository available then you must install these packages before running the Bow Pod DA install script.
librdmacm1 |
lldpad |
mlx5_ib kernel module |
ntp (or other NTP server running on host) |
pigz |
python3-pip |
python3-venv |
rdma-core |
5.2.3. CentOS 7 and CentOS 8 installation and packages
In order to have a stable system where IPU related software can run, the packages listed in Table 5.4 need to be installed on the system. The Bow Pod DA install script installs all of these required packages (the script checks which packages are installed and will download any that are missing). If you are running an offline install without the package repository available then you must install these packages before running the Bow Pod DA install script.
policycoreutils-python (CentOS 7 versions) |
python3-policycoreutils (CentOS 8 versions) |
lldpad |
rdma-core |
librdmacm |
python3 (CentOS 7 versions) |
python36 (CentOS 8 versions) |
chrony (or other NTP server running on host) |
5.2.4. Python packages
All Python dependencies are built-in to the Bow Pod DA install script.