2. IPU-Machine BMC specification
The IPU-Machine baseboard management controller (BMC) runs software based on the OpenBMC project.
The responsibilities of the BMC software stack are to control, monitor and manage system hardware, including power, sensors, inventories and event logging.
You can control and monitor the system, via the BMC, using a variety of user interfaces such as a command line interface (CLI), REST API, IPMI and Redfish.
2.1. BMC subsystem
A block diagram of the IPU-Machine, showing the BMC subsystem, is shown in Fig. 2.2.
The physical components in the BMC subsystem are:
ASPEED AST2520 baseboard management controller
System FPGA
128 MB serial boot flash
1 GB of DDR4 DRAM
One USB port: Micro-USB management interface, see Fig. 13.1
1 GbE management Ethernet interface, eth0, which is configured to 100 Mbps, full-duplex with auto-negotiation enabled on BMC boot
1 GbE internal Ethernet interface, eth1, which is configured to 100 Mbps, full-duplex with auto-negotiation enabled for communication between BMC and IPU-Gateway
Two I2C PSU interfaces for monitoring the state of the power supplies
Five fan interfaces for controlling and measuring the speed of the system cooling fans
Three LEDs used to indicate status
2.1.1. System FPGA
The FPGA is mainly a status and control signal concentrator. It ensures that those control signals are always in a safe state. In addition, it provides hardware monitoring and protection for any thermal or voltage abnormalities. It also controls the sequencing of supply voltages, clocks and reset signals.
2.1.2. LEDs
There are three LEDs used to indicate status:
Green indicates normal operation status
White is used to “locate” or identify a specific IPU-Machine in a system
Yellow indicates various error conditions:
Temperature alert detected
Standby voltages detected failing
PSUs detected failing
Connector domain detected failing
IPU-Gateway 1 domain detected failing
IPU 1 and 2, or IPU 3 and 4 domains detected failing
Fan fail detected (too few fans or fans running too slow)
No profile configuration found in flash
BMC flash not trusted
Note
The white locator LED can be turned on and off with either the CLI or over IPMI.
Using the CLI:
$ ipum-utils locator_led_on
$ ipum-utils locator_led_off
Using IPMI:
$ ipmitool -I lanplus -C 3 -p 623 -U <bmcuser> -P <bmcpass> -H <bmcip> chassis identify <interval>
where <interval> is the time in seconds (default 15 and max 255) that the white locator LED remains lit.
2.1.3. Ethernet switch
There is an Ethernet switch on the IPU-M2000 motherboard that is set up by BMC and can be configured over the BMC CLI or REST interface, to provide different connectivity options between IPU-M2000 components and external network.
Below are description of notable ports of this Ethernet switch with a picture to help visualizing it.
Port 1 : Connected to upper RJ45 connector on IPU-M2000 front panel
Port 2 : Connected to lower RJ45 connector on IPU-M2000 front panel
Port 5 : Connected to BMC Ethernet interface
Port 6 : Connected to IPU-Gateway Ethernet interface
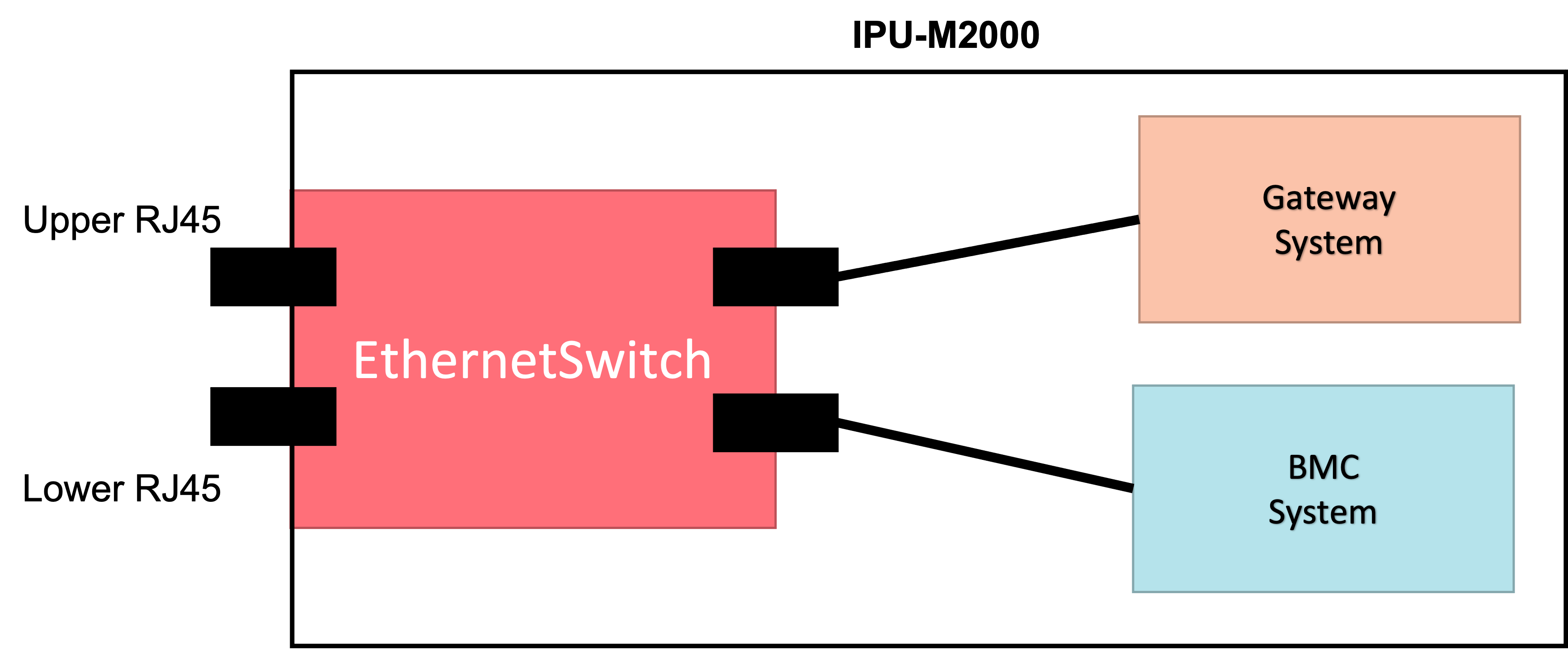
Fig. 2.1 IPU-M2000 simplified Ethernet switch connectivity
This Ethernet switch can be configured in three different forwarding modes with respect to these ports:
BmcOnly: BMC can send and receive traffic to and from port 1 and port 2. IPU-Gateway traffic is blocked.
BmcGatewaySplit: BMC can only send and receive traffic to and from port 2. The IPU-Gateway can only send and receive to and from port 1.
Open (default): BMC and IPU-Gateway can send and receive traffic to and from port 1 or port 2.
You can configure the Ethernet switch to one of the above modes using the BMC CLI as below:
$ ethswitch-fix -s BmcOnly $ ethswitch-fix -s BmcGatewaySplit $ ethswitch-fix -s Open
You can configure the Ethernet switch to one of the above modes using BMC over REST as below:
$ curl -k -X PUT https://<bmcip>/xyz/openbmc_project/ethswitch/mode/attr/Mode -d '{"data":"xyz.openbmc_project.ethswitch.Mode.State.BmcOnly"}' -u <bmcuser>:<bmcpass>
$ curl -k -X PUT https://<bmcip>/xyz/openbmc_project/ethswitch/mode/attr/Mode -d '{"data":"xyz.openbmc_project.ethswitch.Mode.State.BmcGatewaySplit"}' -u <bmcuser>:<bmcpass>
$ curl -k -X PUT https://<bmcip>/xyz/openbmc_project/ethswitch/mode/attr/Mode -d '{"data":"xyz.openbmc_project.ethswitch.Mode.State.Open"}' -u <bmcuser>:<bmcpass>
2.2. BMC functions
The BMC supports the following system management functions:
2.3. IPU-Machine block diagram
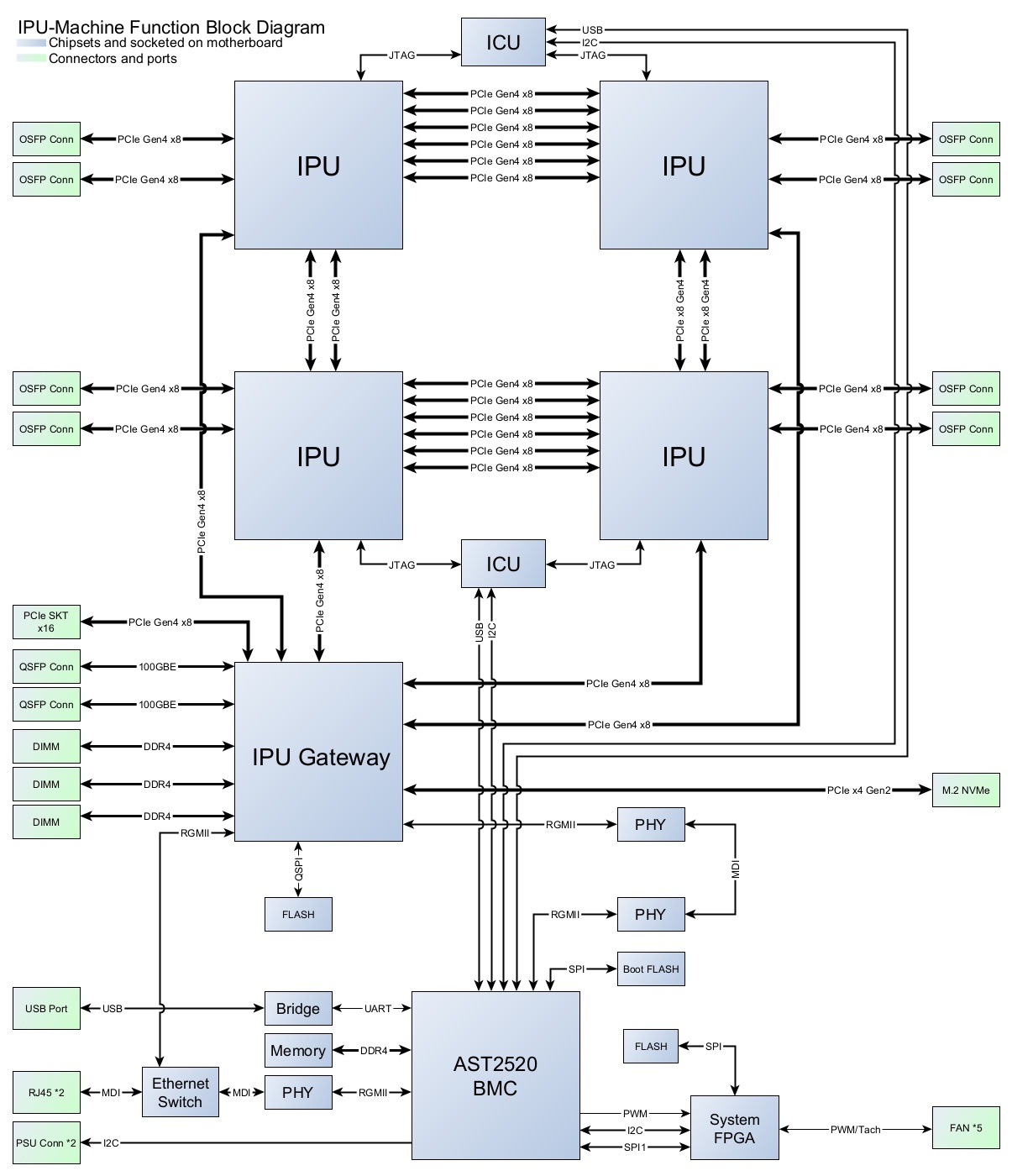
Fig. 2.2 IPU-M2000 BMC block diagram
2.4. Supported IPMI commands
This section summarises the ipmitool commands supported by the BMC. For details of the
parameters and examples of use, see the appropriate user guide chapter.
The BMC is tested with ipmitool version 1.8.18.
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
fru print |
Display information about all FRUs |
fru print <fruid> |
Display information about the FRU with the specified ID |
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
sel clear |
Clear all event logs |
sel list |
Display list of events |
sel elist |
Display list of events with extended information |
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
lan print |
Print network information |
ipsrc dhcp |
Enable DHCP |
ipsrc static |
Configure static IP |
ipaddr <ip_address> |
Set IP address |
netmask <x.x.x.x> |
Set IP address |
defgw ipaddr <ip_address> |
Set default network gateway IP address |
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
power off |
Hard power off |
power soft |
Soft power off |
power reset |
Warm reboot |
power on |
Power on |
bmc reset cold |
BMC reboot |
dcmi power get_limit |
Get current status of power cap |
dcmi power set_limit limit <limit> |
Set new power cap value |
dcmi power activate |
Enable power capping |
dcmi power deactivate |
Disable power capping |
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
sdr list |
Display SDR entry readings and their status |
sdr elist |
Display extended sensor information |
sensor thresh <sensor_name> lcr <value> |
Set sensor lower critical threshold |
sensor thresh <sensor_name> lnc <value> |
Set sensor lower non critical threshold |
sensor thresh <sensor_name> unc <value> |
Set sensor upper non critical threshold |
sensor thresh <sensor_name> ucr <value> |
Set sensor upper critical threshold |
sensor list |
Display sensors and thresholds in a table format |
sdr get <sensor_name> |
Display sensor information |
sdr type |
Display a list of sensor types |
sdr type <sensor_type> |
Display SDR repository records of a sensor type |
Note
Sensor thresholds values in sensor thresh command should match this equation: lcr <= lnc <= unc <= ucr
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
sol activate |
Access serial over LAN (SoL) interface |
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
sel time set “DD/MM/YYYY HH:MM:SS” |
Set time and date (will fail if system is in NTP mode) |
sel time get |
Get time and date |
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
user summary [<channel_number>] |
Print a summary, including number of users on the system |
user list [<channel_number>] |
List users |
user set name <user_id> <username> |
Create a user with <user_id> and <username> |
user set password <user_id> [<password> <16|20>] |
Create a password for user with <user_id> (the password can be 16 or 20 bytes in length) |
user enable <user_id> |
Enable user with <user_id> (must be done after creating user and password) |
user disable <user_id> |
Disable user with <user_id> |
user priv <user_id> <privilege_level> [<channel_number>] |
Set privilege level for user with <user_id> |
channel setaccess <channel> <user_id> ipmi=on |
Enable IPMI access for a user |
The maximum number of system users is 30
The maximum number of users with IPMI access is 15
The maximum username length for an IPMI user is 16 bytes
User IDs are from 1 to 15
Passwords must be a minimum of 8 characters in length
The privilege levels are:
0x1: Callback
0x2: User
0x3: Operator
0x4: Administrator
0x5: OEM Proprietary
0xF: No Access